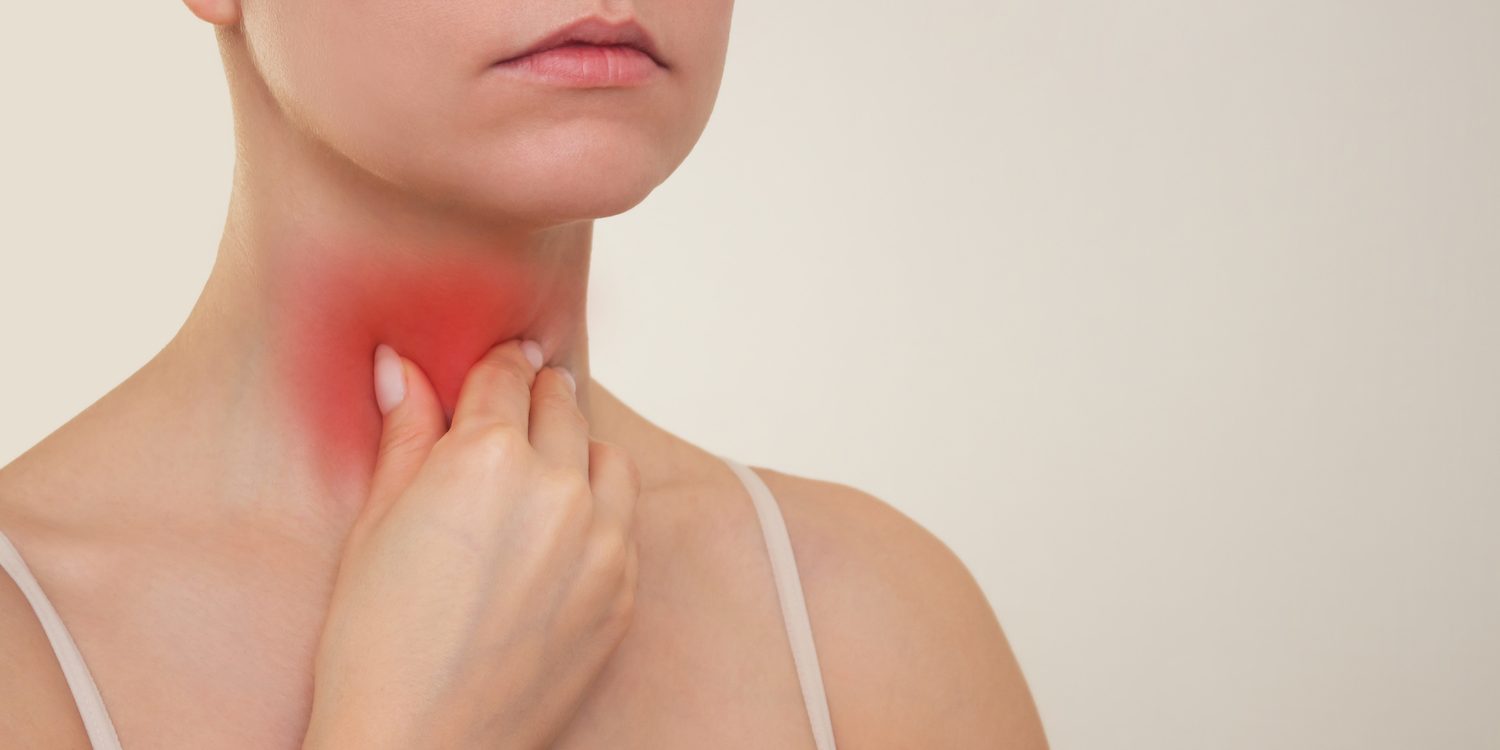
Pharyngitis is a widespread condition characterized by inflammation of the pharynx, the back of the throat that lies above the esophagus and larynx. This condition causes pain, discomfort and itching in the throat and is often a symptom of an infection, which can be either viral or bacterial in origin. It occurs with increased frequency during the winter months. Pharyngitis can present with severe symptoms, so early diagnosis and treatment is vital.
Pharyngitis: What causes it
Pharyngitis, commonly known as sore throat, is mainly caused by infectious agents, more specifically viruses and bacteria. Viral pharyngitis, the most common type of the condition, is often a consequence of infection with viruses such as rhinovirus, adenovirus, influenza, the Epstein-Barr virus that causes infectious mononucleosis, or the coronavirus. These infections are usually part of a wider upper respiratory tract infection and are highly contagious.
Bacterial pharyngitis, although less common, is primarily caused by the streptococcus bacterium, which is a common cause of acute pharyngitis. In some cases, pharyngitis can also result from conditions such as allergic rhinitis, sinusitis or gastroesophageal reflux, while exposure to cigarette smoke also acts as an aggravating factor. Understanding the underlying cause of pharyngitis is vital as it determines the course of treatment and management. In addition, identifying the cause helps to implement appropriate preventive measures to limit the spread of infectious agents.
Pharyngitis and symptoms it causes
Pharyngitis manifests itself through a series of symptoms that vary in intensity. The main symptom is a sore throat, which is especially noticeable when swallowing. Symptoms also include redness of the pharyngeal walls and swelling of the cervical lymph nodes. Other associated symptoms may vary depending on whether the pharyngitis is viral or bacterial in origin. Viral pharyngitis often presents with a runny nose or difficulty breathing through the nose, cough, sneezing, mild fever or chills, and general tiredness or weakness. In contrast, bacterial pharyngitis can present with high fever, chills, myalgia and sometimes with the appearance of purulent spots on the tonsils. In some cases, especially in children, abdominal pain and rash may occur. Symptoms become particularly severe on the 3rd-5th day and usually subside within 10 days.
Diagnosis and treatment for pharyngitis and its symptoms
The diagnosis of pharyngitis is based on evaluation of symptoms by taking a detailed medical history and physical examination findings. The physical examination includes an overview of the nasopharynx and ears, as well as palpation of the cervical lymph nodes. Additional tests such as laryngoscopy and throat swab culture are also particularly helpful. Laryngoscopy facilitates a detailed assessment of the pharynx and larynx area, while taking a pharyngeal swab for culture is primarily used to detect strep (strep test). Finally, carrying out blood tests allows the detection of an infection or virus in the blood, such as the Epstein-Barr virus.
The treatment of pharyngitis varies according to its etiology, as the treatment plan differs depending on whether the condition is caused by a virus or a bacteria. For viral pharyngitis, which makes up the majority of cases, treatment is aimed at managing symptoms, as antibiotics are ineffective against viruses. Patients are encouraged to take over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen, consume throat lozenges, and gargle with saline. Adequate hydration and rest are also recommended to boost the immune system.
In cases of bacterial pharyngitis, mainly streptococcus, antibiotic treatment is prescribed for 7 to 10 days. Completing the full course of antibiotic therapy is vital to prevent complications or recurrences. Patients are also advised to avoid irritants such as cigarette smoke and to observe good hygiene practices to prevent the spread of infection. For recurrent or chronic pharyngitis that causes frequent symptoms, especially when associated with factors such as allergic rhinitis or GERD, treating the underlying condition is key to getting the pharyngitis to go away. ENT Surgeon in Athens Dr. Olga Papadopoulou successfully treats pharyngitis and the symptoms it causes, focusing on eliminating the infectious agent responsible for its occurrence.